 FCA and PRA licenses (authorisations) and ongoing compliance support, training, recruitment. Contact us 7 days a week, 8am-11pm. Free consultations. Phone / Whatsapp: +4478 3368 4449 Email: hirett.co.uk@gmail.com
FCA and PRA licenses (authorisations) and ongoing compliance support, training, recruitment. Contact us 7 days a week, 8am-11pm. Free consultations. Phone / Whatsapp: +4478 3368 4449 Email: hirett.co.uk@gmail.com
EMI Application Form; Section: 4 and 5
1.0 Executive Summary
Currently HIRETT is functioning in the Money Services Business sector as an Authorized Payment Institutions and directing to provide quicker and stress-free E-Money & payment services for its clients/Customers to worldwide. The aim of HIRETT is to generate a stress-free access to the services to the clients/Customers so that residences in UK and European Union are sending and paying money through authentic way via online platform. To Make the customers life easy, Hirett t/a Hirett will launch E-money card so that customer can pay by their card for remittance. Also customer will be able pay for their daily expenditure using E-money Card. In addition to E-Money card, We are intended to provide another payment services very similar to our competitor GoCardless. HIRETT will collect payments through Direct debit mandate using a full pledge electronic system on behalf of Retailers or other firms from their customers on re-current and periodic basis. We are avoiding Cash transactions totally and aiming a cashless economy. The directors of Hirett Ltd are aiming to expand its business consistent with our marketing approaches and this business plan is focusing on the issues relating to the business development. It also focuses on the marketing plan, financial management plan, Risk assessment and internal control.
Based on the size of our market and our defined market area our sales projections for the first year are around € 20 million.
2.0 Depiction of Business
2.1 Introduction
HIRETT is incorporated company which will be trading for E-money and Payment Services. The company has effectively been run by [Name]. [Name] has been doing business as Authorized payment institution with MLR registration and FCA Approval. He has run the HIRETT with maintainable profit margin. As a plan to develop the Payment Services business [Name] has intends to trade as an Authorized E-Money Institution to facilitate faster transfer using E-money Card and accommodate towards worldwide remittance and Payment services markets apart from its traditional ethnic community based money transfer after approval.
Company Details
Company Name: HIRETT
Company Number: 00000000
Incorporation Type: Private Limited Company
Registered Address: [Address]
Trading Address: [Address]
Email: info@gmail.com
MLR Reg. No.: n/a
Current Regulatory Status: Authorised payment institution FRN (FCA Register): 123456
Proposed Regulatory Status: Authorised E-money
Key Individuals
Managing Director [Name]
IT Director [Name 1]
Nominated Officer: [Name]
The Company, HIRETT.
| Location | [Address] |
| Year Established | [Date] |
| Industry | E-Money/Payment Services |
| Founder | [Name] |
| Website | [Website] |
HIRETT t/a Hirett (also referred to as “Hirett” or “HIRETT”) is an existing Payment Processing Provider that offers customized payment Solutions to allow Customers/businesses to remit money worldwide. Hirett has been in operation since in 2015, and has reached several milestones since its launch. These milestones include:
- Licensed and regulated as a Authorized payment institution in [Date]
- Licensed and regulated as a Authorized payment institution in [Date]
- Submitting application to become an Authorized E-Money Institution in Q4
Objectives
Today, Hirett seeks to expand its offerings to include several new services including new types payment services like collecting payments on behalf of other firms from their customer, and issuing E-money card possibly issue Sort-code and account no like The Tide platform. As a result of these services, the Company seeks to reach the following objectives over the next five years:
- To sign on 1000 business clients in it’s first year, growing to over 7000 by the end of Year 5 as follows;
| Services By Years No of Target Customers/clients | ||
| Payment Collection via Direct Debit | 5 | 2000 |
| Remittance | 5 | 3000 |
| E-money card/Account | 5 | 2000 |
| Total | 7000 | |
Company Values
HIRETT operates with a high standard of excellence, and is fully devoted to exceeding the expectations of its clients.
Mission Statement
“Making Payments and remittance Easier”
Vision Statement
“To create new opportunities for providers by offering payment services to businesses of all kinds – especially to those who are considered low margin customer and ignored by high street large banks.”
Ownership Structure
The Company is owned 00% by [Name], 00% by [Company Name].
Products and Services:
Definition of E-money:
Electronic money is one of the means of payment, which is stored on an electronic device. This definition emphasizes that payments must be made in electronic form. In this regard instead of the term “cash value” the term “electronic value” is often used. (EC Directive on electronic money, 2009) Electronic money is a means of payment, emitted by pre-existing funds. The value entered in a cash payment is equivalent to the value of issued electronic money. Purchase of electronic money means buying cash value. Electronic money is a means of payment which is accepted by third parties (institutions, enterprises and individuals) other than the issuer. This means that the holder of electronic money should be able to use them to purchase goods and services from a wide range of people. For example, the electronic value which is released by the employer for his workers and can only be used to purchase meals in the dining room of the employer is not electronic money.
Electronic money is stored in a special device, usually on the hard drive of your PC or a microprocessor card, and that can be transmitted from one device to another using telecommunication lines and other electronic media. (Serge Lanskoy, 2000, p. 30) In economic terms “electronic money” is a payment instrument, which has, depending on the implementation of the scheme, the properties of both traditional cash and traditional payment instruments (credit cards, checks, etc.)
Electronic money is divided into two types: based on the cards (card – based) and on the basis of networks (network – based). In turn, the first and the second group fall into the anonymous system, allowing carrying out operations without user identification. Non-anonymous system, require mandatory identification system participants. ([Name], 2008, p.5) Most famous card-based systems are Mondex, Proton, CLIP, and VISA Cash. E-money based systems are: WebMoney, Yandex (in Russia), Cash, Paypal, E / Gold, RUpay, e / port, Rapida. Most systems are not anonymous.
This Business Plan reports the future business and functioning approaches of HIRETT LTD, a E-Money Institution (EMI). Commercial Banks have limited knowledge in the EMI sector, or have
limited resources to cater EMI clients. Dispersed customers and lower margin of customers are deemed as reason behind unattractiveness of EMI to large commercial banks. Furthermore, the increased level of regulation for anti-money laundering (“AML”) compliance has restrained Banks from entering or continuing to provide services to the MSB/EMI sector.
As [Name] has Years of experience in remittance services business, So HIRETT LTD will have predominant customer base, established remittance channels and operational infrastructure to run remittance business and E-money.
Currently, Hirett offers a full line of services that allows businesses to simplify the way that they process payments. Hirett will offer secure E-Money Account and accepts payments in and out from all major Banks/other E-Money.
E-Money Account:
E-money institutions tends to serve the individual and business customer which have been refused by high street commercial banks for various reason by issuing E-money card and account no a sort code to receive payments and pay their bills. Even Money services businesses tend to concentrate in the UK, Africa and South and North America corridor remittance market with a view to expand worldwide, where HIRETT LTD will be operating as E-Money which will facilitate customers issuing E-money card and account no to receive and paying to different parties similar to the Tide Platform Ltd.
Hirett will offer a quick and simple solution that allows businesses to easily apply and be approved for E-Money Account. E-Money Account allow businesses to receive payments and authorize payments out by using E-money card and Account.
- Online Payment account: By simply installing Hirett’s EMI Mobile Apps or web based account opening applications, clients can quickly begin processing payments online. Hirett’s gateway solution allows them to create a virtual terminal and secure payment page, bulk process high numbers of transactions, and deal in multi-currencies.
- Risk Management Solutions: With over 120 integrated risk management tools, HIRETT ensures that clients are freed from any potential fraudulence or security issues. These tools can be applied to transactions involving e-commerce, remittance, adult entertainment, multi-level marketing, travel, pharmacy, dating, gaming and gambling, and more. Hirett’ sophisticated tools are properly designed to execute both basic, intelligent, and third-party risk
The HIRETT platform is backed by several third-party integrations that strengthen security and maximizes the platform’s potential. These integrations include:
Tokenisation: Eliminates the risk of hackers and security breaches by using tokens to replace highly sensitive data such as card numbers, eWallet login IDs, and bank account details. Tokensation removes its clients’ regulatory burden by ensuring that no valuable customer information can be mismanaged or misused.
Additional Features:
- Raise sales invoices, personalise them with customer/clients logo and send by email
- Send invoices to clients phone contacts
- Make payments from within the app
- Transactions are categorised as they happen to automate bookkeeping
- Attach files and add comments to transactions to help with expense management
- Link Harmonnie to Stripe, and Xero, as well as other cloud-based accounting systems
- App security includes a 4 digit passcode and a face recognition system that can be used during high-value transactions
- Contact the Hirett support team via Mobile App
Direct Debit Solutions:
In addition, HIRETT will collect payments on behalf of Retailers and others firms from their customers using direct debit mandate like Gocardless.
Remittance Solutions:
Even HIRETT will also continue remit money on behalf of Small, Authorized payment Institution and other corporate clients who needs to send money in large scale specially travel Business, Export and import, multinational companies who has operation worldwide.
Remittance:
In 2015, HIRETT LTD t/a Hirett also launched Hirett Payments; a remittance platform that allows customers to send money internationally in a fast, convenient and secure manner. Hirett Payments offers several remittance services including Money Transfer, School Fees Payment, Airtime Topup, and Hospital Bill Payment.
Key Success Factors

As the Company expands its offerings to include Direct Debit Solutions and E-money Account, it will be important that several key success factors are met. Specifically, Hirett must gain the proper approvals and licenses to offer its services, and must implement a secure and profitable process to ensure that risk is managed for the high-risk businesses that it will serve.
While high-risk accounts have much larger profit margins, the risk to E-Money Accounts Services is much lower. For this reason, many processors will provide services to a E-money institutions that they deem as being “low-risk”.
If the Company can meet these factors, success will be expected. Not only does the brand have proven experience as a E-Money Accounts Services and Payment services provider, but these new services will also allow the Company to fill a major gap that is avoided by many operating payment processing companies and Commercial Banks.
2.2 Summary of financial forecast and Approach to market:
The financial projection for the HIRETT shows its prospect and opportunity is very bright in market. The three (3) years financial projection shows that the growth of the business is smooth and steady. The following profit figure shows the profitability of HIRETT is well efficient.
Productivity figure:
| Years | Income £ | Expenses £ | Net profit before Tax | Net profit % |
| First Year | 258,787 | 227,494 | 31,293 | 12.09% |
| Second year | 305,855 | 235,203 | 70,652 | 23.10% |
| Third year | 336,544 | 241,117 | 95,427 | 28.35% |
The profitably figure shows that the profit is growing fast due to the marketing and efficient people in the management. Third year profit is radically increasing because it is operating in EU.
The three (3) years financial projection shows that the project is profitable. HIRETT’s prime target market is E-Money Accounts, Payment services like Direct Debit Solutions and remittance to work in Europe and worldwide because payments services have emerged as a key driver of economic growth.
There is a good economic relationship among UK, EU and rest of the world. Some very Basic indicators which are characterize the trade and investment co-operation among UK, EU and rest of the world.
Revenues from remittances now exceed various types of foreign exchange inflows, particularly official growth assistance and net earnings from exports in these countries. The bulk of the remittances are sent by EU, and Third world countries migrants workers rather than associates of the EU and other Migration.
Robust remittance inflows in recent years have been instrumental in maintaining the current account surplus despite widening a trade deficit. This in turn has enabled EU, and rest of the world to maintain a growing level of foreign exchange reserves.
√ Each additional migrant’s worker brings in $1000 remittances annually;
√ Remittances are higher during periods of low economic
Payments Services tend to locate in heavily populated areas that are less affluent and/or have a large immigrations population. In many cases, these areas are underserved by Banks and a significant portion of the population is “un-banked”. Cases where the MSB/EMIs are the only form of access to the international payment system are not rare.
HIRETT will limit its powers to those activities described in the Business Plan. As a special purpose Company operating under the Business Plan, HIRETT will offer its services to the general public either on a wholesale or retail basis in the ordinary course of business.
The application request to become an Authorised E-Money Institution has been taken by senior management in the belief that Europe can offer an amplified volume in their payment and remittance statistics and upsurge their cash flow. The location of the business allows for niche markets to be exploited and using the passport as a way to spread the word into European based different communities and also be able to offer the EU, and rest of the world payment corridor to other payment institutions.
As a necessary part of their business, EMIs must have access to the international payment system to transact their business. HIRETT will be structured to serve the needs of firms operating as registered EMIs.
The Board of Directors and senior management have the experience necessary to launch and successfully operate the Company. The Director of HIRETT., [Name], has direct knowledge of the MSB industry, extensive experience, and professional administration skills. [Name] has direct relevant experience in the industry. In addition to his functional organization experience, HIRETT intends to influence this MSB expertise through a range of cooperative relationships with MSB/EMI partners, The breadth of experience possessed by senior management and the Board of Directors will enhance the Company’s ability to provide the necessary guidance for HIRETT to operate successfully and to prudently manage its market penetration and servicing of customers in the EMI industry niche. The Company believes that it has the capacity to become a recognized industry leader by emphasizing the following competitive advantages:
√ Superior focus on customer retaining in the UK and obtaining new customers in the UK and Europe.
√ Inability or lack of desire by banks to adequately serve this niche
√ Joining relationships with third-parties and customers
√ Exceptional internet presence that is positioned to serve clients
√ Maintenance of a high-quality, real-time financial information structure
The Company’s market niche will be EMIs that demonstrate ongoing compliance with AML regulations and wish to maintain a relationship with a financial institution that understands their marketplace.
Along with highly qualified and knowledgeable employees, prominent technology solutions are one of the keys for a financial institution to effectively compete in the increasingly competitive market and HIRETT believes this will be true for the Company HIRETT LTD will utilize a proven technology platform that will enable the Company to deploy products quickly and efficiently to its customers and will provide a stable operational platform to allow the offering of a selective group of targeted products and solutions.
2.0 Market Research and Market Niche of the Business
2.3.0 E-money market trends
The advancement in digital technology has welcomed many new trends over the last couple of years, and the payment industry is constantly evolving and adapting to keep pace. In 2014, we moved further towards a cashless society, and I believe this will continue in 2015, with a further decline in conventional retail banking.
Digital services such as e-money accounts with linked debit and prepaid cards are quickly emerging as popular alternatives to traditional banking, not just in the UK, but around Europe and the rest of the world.
The knock-on effect from this will result in a major shift this year, from current favoured online payment methods like credit cards and PayPal, to a broader set of online and mobile payment options. These will not only accommodate changes in the UK banking market, but also payment preferences from consumers beyond UK shores looking to purchase goods from British e-tailers.
E-money
With consumers constantly looking for increased speed and ease of use, they will gradually turn to e-money accounts, which offer the benefits of a traditional bank account with the addition of increased privacy, reduced charges, faster responses and improved consumer interfaces.
As the payment landscape continues to heat up, e-money accounts with linked prepaid cards have evolved and will encapsulate a new market of prospective users. I predict prepaid cards will become an important asset to the average consumer, proving to be a useful alternative to traditional credit and debit cards.
For some, they can ensure their money is budgeted more wisely and for others, businesses and consumers alike, they offer a secure alternative for making wage transfers and for allocating employees with company cards.
This signals change for traditional banking methods, as consumers increasingly move to online funds management – the need for personal interaction has been removed, thus causing the decline
in bank branches. Conventional banking methods will become redundant, with e-money accounts and prepaid cards shaping the payment marketplace of the future.
Global E-Money Review 1:
The EU has the most structured and regulated market in the world with the UK through the FCA having the most comprehensive regulation and authorisation procedures. It is not surprising then that there is currently a rush of non-banks moving into the business of E-money products each one arriving with a new USP or channel to market into. That said it is still so new that market penetration to the consumer is very low. Being regulated in the UK also enables the business to be passported across the rest of the EU. The EC Review shows clearly how popular the UK has been with now over 112 EMI’s and over 150 small issuers. Only the Czech Republic approaches this with 24 small issuer waivers granted, but on closer inspection the majority of the latter are to transport systems, as each transport system has its own E-money product which is run under a waiver. Of the waived businesses in the UK the majority are aimed at youth, open loop gift cards in a restricted scheme (as allowed by the regulations), gaming and adult entertainment markets. They are anonymous and can be used online without fear of ID Fraud or detection; are quick and easy to offer and make a profit out of Distribution, can be purely on-line as a virtual account; uploaded onto a mobile phone, purchased on the high street as a scratch card or even just unique number generated at an EPOS. They are low cost and can therefore still generate good profits despite the low margins available. Whilst looking at E-money there are also those products which fall outside the definition of E-money (particularly closed loop gift cards), but which should nevertheless be considered to be E-money as, in reality, that is what they are.
The latest development in gift cards is the advent/arrival from the USA of the Gift Card Malls. These will be appearing from November this year in supermarkets, petrol stations, stations and in shopping malls. Effectively these are distribution points for gift and other pre-pay cards and would be an ideal distribution point for any transport related E-money proposition. These cards are taken from a stand which will typically offer between 40-100 different cards (store gifts, activity fits, petrol cards, general pre-pay cards, travel cash, etc etc). When the customer takes the card to the till and pays by cash or credit/debit card, the shop assistant passes the card through the EPOS to load the value that has been paid for. It is expected that the amount of these so called “gift card malls” will move the uptake of E-money products to the next level.
2.3.1. Regional Remittance Trends 2
The outlook for remittances in East Asia and the Pacific has worsened due to a weak global economy. Growth decreased from 4.1 percent in 2015 to 2.1 percent in 2016, with the Philippines likely to see the slowest expansion in a decade.
Remittances to Europe and Central Asia are estimated to fall again by another 4 percent in 2016. This is however much less substantial than the decrease of 22.5 percent seen in 2015. Some countries in the region, including Bulgaria, Montenegro and Bosnia and Herzegovina can still expect to see modest remittance growth.
Latin America and the Caribbean saw remittance flows into the region increase in the first half of 2016, due mainly to a recovering U.S. economy. Remittances to the region are expected to grow by
6.3 percent and reach $72 billion by the end of 2016.
Remittances into the Middle East and North Africa are expected to increase by 1.5 percent in 2016 but remittances from GCC countries are expected to decline Beyond 2016, remittance are expected to pick up only gradually.
This year the South Asia region would see a decline of 2.3 percent in remittances to the region due mainly to the impact of declining oil prices and labor market nationalization policies on remittances from GCC countries. Moving forward remittance growth in the region is expected to remain subdued.
Remittances flows to Sub-Saharan Africa are expected to decline by 0.5 percent in 2016. For 2017 remittances are expected to grow at 2.5 percent, underpinned by flat remittances in Nigeria which account for two-thirds of remittance flows into the region.
The top recipients of remittances are, in nominal US dollar terms, India, China, the Philippines, Mexico and Pakistan and, in terms of remittances as a share of GDP, Nepal, Liberia, Tajikistan, Kyrgyz Republic and Haiti (figure 2).
Figure 1: Remittance Flows Are Larger than Official Development Assistance (ODA), and More Stable than Private CEMItal Flows3
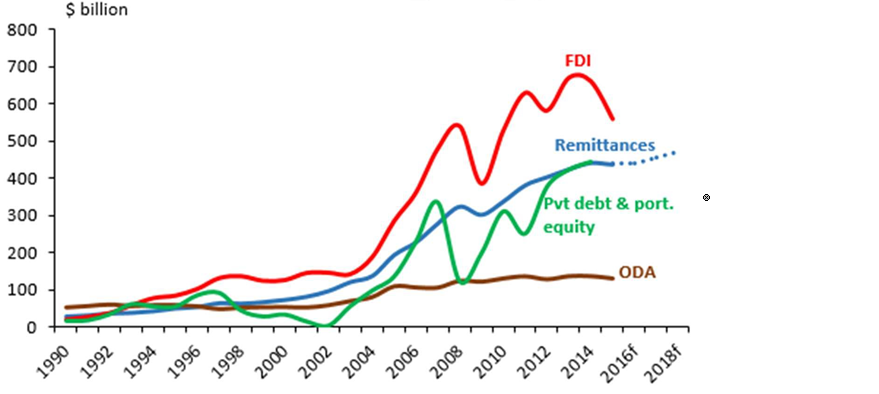
Figure 2: Top Recipients of Remittances
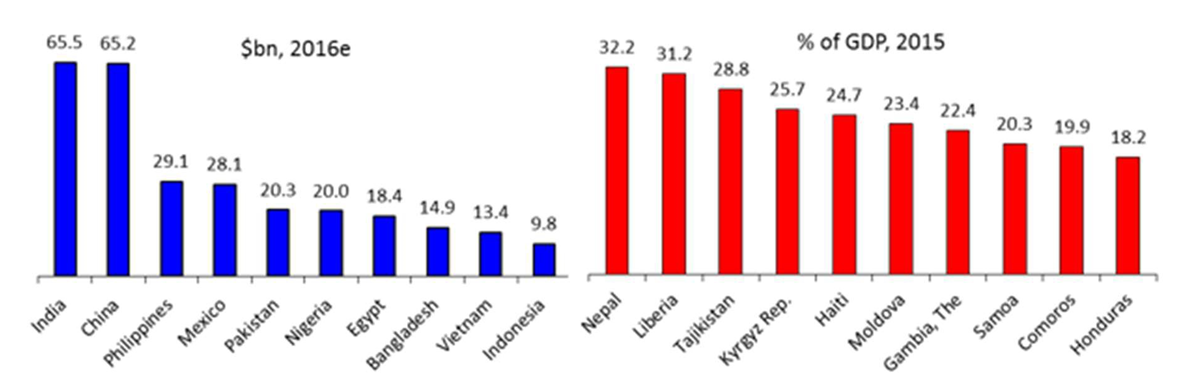
Table 1. Estimates and Projections for Remittance Flows to Developing Countries 4
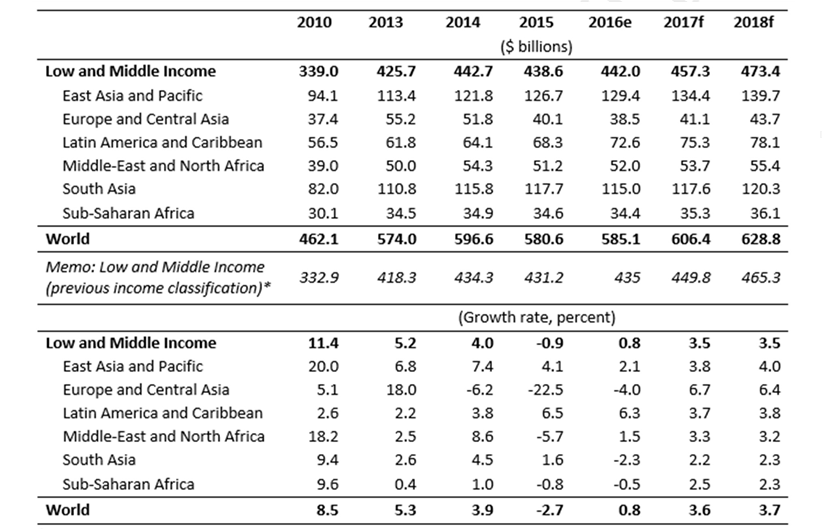
* This group excludes Equatorial Guinea, the Russian Federation, Venezuela and Argentina which were classified as High Income.
Latest Industry Trends
Hirett Mobile Solutions seeks to become a leading brand in payments for both businesses and individuals, worldwide. To do so, the Company will seek to expand its services to enter two new financial payment sectors: Global Remittance.
Global Money Remittance
Money remittance platforms have increased in popularity as individuals have moved towards the internet to send money to their family and friends back home. Money which migration send back to developing countries now officially totals over $440 billion each year, according to the World Bank. However, experts say that the market is likely worth far more considering the value of transfers which flow through unrecorded channels. Remittances, delivered either though formal or informal channels, are credited with reducing poverty and aiding the poor in developing countries.
Often, remittances are the first form of aid to reach disaster hit countries. In 2016, the top remittance recipients worldwide were India, China, the Philippines, Mexico, Pakistan and Nigeria. As a share of GDP though, the top five recipients were Kyrgyz Republic, Nepal, Liberia, Haiti, and Tonga. Due to many factors, global remittance decreased over the last several years, but is expected to rise steadily in 2017 and beyond. The current status of the global remittance sector is explained below, by region (Migration and Remittances: recent Developments and Outlook, 2017):
- Latin America and the Caribbean was the only region to see growth in remittances in 2016. Remittances to this region equaled $73 billion; an increase of 6.9% over 2015. This growth was driven by a strong U.S. labor market and beneficial exchange rates. The countries leading the growth in these regions include Mexico, El Salvador and Guatemala. The region’s remittances are expected to grow by 3.3% to $75 billion in
- South Asia’s remittances declined by approximately 6.4% to $110 billion in 2016. Experts believe that this decline is a result of lower oil prices and fiscal tightening in the GCC countries. However, while there was a decline in remittances to India, Nepal and Bangladesh; Pakistan saw a modest growth of 2.8% in the same year. Remittances to the region are expected to grow by 2% to $112 billion in
- The MENA region (Middle East and North Africa) saw an estimated decline of 4.4% to $49 billion in 2016. This region’s decline was driven by Egypt, the region’s largest remittance recipient. Remittances to this region are expected to expand by 1% to $52 billion this year.
- Sub-Saharan Africa declined by 6.1% to $33 billion in 2016, due to slow economic growth in remittance-sending countries; decline in commodity prices (such as oil) which negatively impacted remittance receiving countries; and diversion of remittances to informal channels due to controlled exchange rate regimes in countries such as Nigeria. Remittances to this region are expected to increase by 3.3% to $34 billion this
- Remittances to Europe and Central Asia were heavily affected for a three-year stretch between 2013 and 2016. This led to a 4.6 percent decrease to $38 billion in 2016. The decrease was due to low oil prices and sanctions that continued to impact Russia, which is both a major recipient and a remittance-source country. In 2017, remittances to the region are expected to increase by 6.6% to $41 billion, mostly due to stronger growth in Russia and several other European
- East Asia and the Pacific region realized a decline of 1.2% in 2016 to $126 billion. Flows to major recipient countries were mixed, with the Philippines growing by almost 5% while Indonesia fell by 4.4%. In 2017, it is expected that remittances to the region will grow by 5% to $129 billion.
In line with the global economic outlook, remittances to developing countries are expected to grow on average by 3.3% in 2017, to reach $444 billion. However, the cost of sending money continues to be extremely high and well above the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target of 3%. According to the Remittance Prices Worldwide database, the global average cost of sending remittances of $200 remained at 7.45% in the first quarter of 2017 (Migration and Remittances: recent Developments and Outlook, 2017). Sub-Saharan Africa continues to have the highest costs, averaging above 10%. This is due to low volumes of formal flows, inadequate penetration of new technologies, and lack of a competitive market environment (Migration and Remittances: Recent Developments and Outlook, 2017).
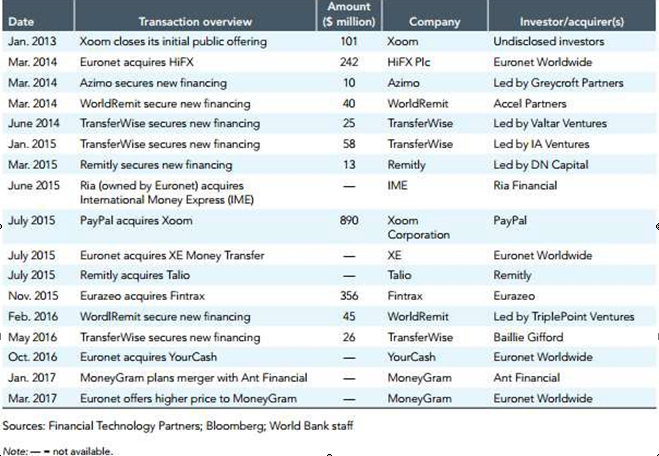
Money remittance continues to be a popular sector for investments, as several industry mergers and acquisitions have taken place throughout the past several years. The table above displays several of these mergers; with some acquisitions amounting to over £890 million (Migration and Remittances: Recent Developments and Outlook, 2017).
2.3.2 The Remittance Marketplace in the United Kingdom
Remittances are defined as regular person-to-person and Company to Company international money transfers.
UK remittances market: Migration to the UK5
The UK is a major host of migration, and London remains a global centre for migration with approximately 3.8 million residents, out of a total population of 8.65 million, born outside of the UK. According to the 2011 census the foreign born population of the UK was estimated at 7.5 million. A significant proportion of the foreign born population is believed to send remittances from the UK,
which were an estimated USD 2,222 million in 2013, driving the demand for money transfer services in the UK. The immigration is fluctuating yet continuing immigration into the UK, with over 600,000 arrivals over 2010 and 2011. The top ten key receivers of remittances from the UK are illustrated in Figure 3.
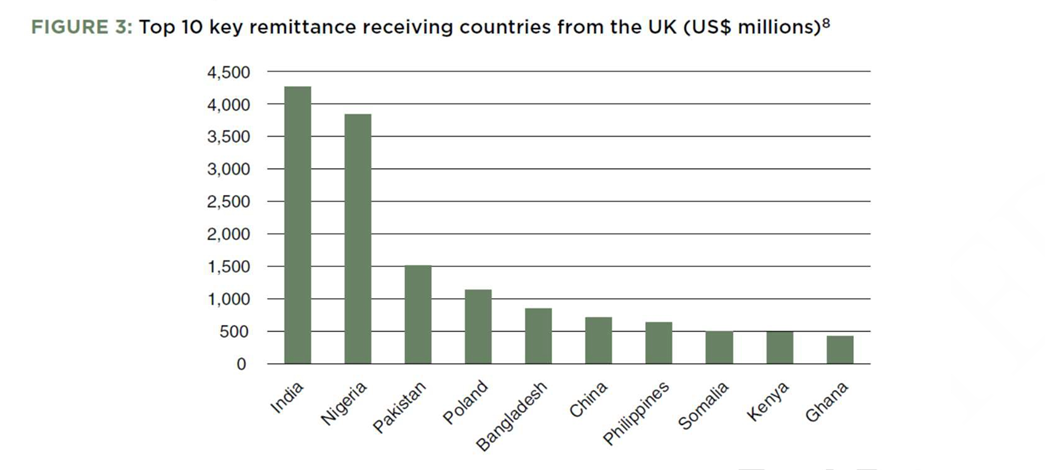
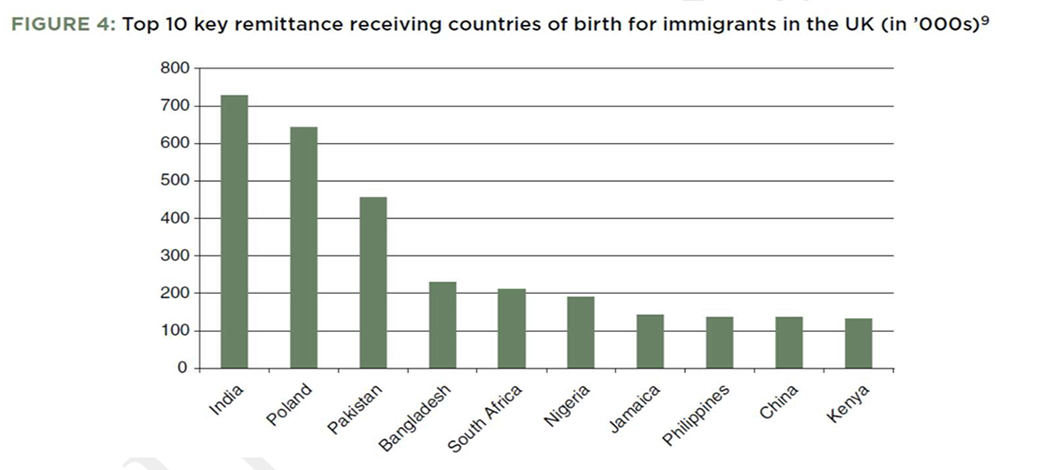
These ten corridors reflect many of the top key country miHirett communities in the UK (including from developing countries), illustrating the link between the size of the miHirett community and the size of the flow of remittances (Figure 4).
The UK remittance market is relatively competitive and offers consumers a range of services, from the traditional ‘cash to cash’ products through agents, transfers to and from bank accounts, as well as online and mobile services. The regulatory environment for remittance services in the UK has been geared towards encouraging competition. There are a number of MTOs who serve a broad range of communities sending money home. Whilst the regulatory regime is relatively open, allowing small corridor specialists to flourish alongside global MTO s, the broader global regulatory environment is becoming increasingly difficult for large numbers of non-bank remittance services providers (RSPs) to continue providing remittance services on behalf of their clients.
Several UK banks have been in the process of ‘de-risking’—no longer providing banking services (and therefore access to the international payments system) to clients that they consider high-risk, such as those providing money transfer services internationally. This has meant that non-bank RSPs that have lost their bank accounts have had to find alternative arrangements in order to continue operations. This challenge has come to the attention of development stakeholders and is a great concern, particularly for countries such as Somalia, where remittances are an important lifeline in an environment that lacks formal banking infrastructure. In addition to providing greater insight into senders’ behaviors and financial inclusion levels, the research also provides some intelligence on whether the shifts in the UK remittances market as a result of this de-risking has had a marked impact on consumers.
- The money goes to Asian sub-continent, the Caribbean, Africa, China and Eastern
- The scenery is changing though. There is heightened interest in remittances as a result of a growing awareness of the global market. This, combined with an increased in the use of new technologies in the financial services arena, has meant that there are a number of ‘new technologies’ that are being applied to remittances.
- One of the key benefits which could arise from improving the remittance environment and financial inclusion in the UK for migration is that it could lead to an improvement in the financial inclusion environment in the migration’s home country. In particular as financial literacy improves in the UK this knowledge will be transferred to the communities at home.
- Remittances are currently sent in a variety of forms including cash-to-cash, account-to- account, cash-to-card, card-to-card, cash-to-mobile phone, mobile phone-to-mobile phone, cash sent through the post and cash that is hand carried by a friend or relative. Similarly, with respect to the size of the market, there is no official information on how much is sent though each method. Indeed, at least two of the methods would be termed informal and are even harder to measure.
- However, market experience and feedback from the various operators’ leads to the conclusion that the majority of remittances are sent by cash-to-cash, with cash via friends and other informal methods making up the most of the remainder. Cash-to-account would be the fourth most used method.
- This section will list then types of organization’s that send money, examine the key methods used across the remittance industry, describe the business models and draw out some of the key facets of the business model of each one.
2.3.3 Organizations providing remittance facilities
- Banks – for the purposes of this document banks are taken to be account holding institutions that have the ability to offer services based on the ability to provide money transfer services for customers with whom they have a pre-existing relationship.
- RSP – Remittance Service Provider – an organization that provides/own a remittance Distribution of the service is via its own locations, networks of agents and other methods including internet and Mobile Applications based remittances. Examples include Western Union and MoneyGram.
- MSB – Money Service Business – an outlet where a consumer can go to transfer money. An MSB may have its own money transfer service or be an agent for an RSP. Each MSB is registered with HM Revenue and Customs.
- Phone operators – organizations that provide messaging and technology solutions that enable the transfer of funds via a mobile phone.
- HIRETT intends to serve the payment needs of entities in the MSB sector and to provide a convenient means of clearing transactions from their customers and permitting these businesses access to payments systems and the Forex market. These services will be provided consistent with the need to ensure that effective controls are implemented to prevent violations of AML regulations along with consulting and independent review (by Third Party) of MSB compliance programs. The Company will place particular emphasis on personal service and information accessibility.
What Does This Mean for Hirett?
Hirett is currently expanding into the market with several new services at a time when it’s offerings will be most effective. As global remittance returns to its former levels, HIRETT will introduce Hirett’s; an online remittance platform that offers transfers at a fee of only 1-1.5% per transaction. While many consumers deal with extremely high fees of 7-10% (or more), Hirett will offer a lower-cost solution that allows recipients to keep more of their money on each transaction. As a result, Hirett expects to grow its user-base quickly, which will allow for a strong exit consideration while investment into the sector is heavy.
2.4 Target Marketplace
Based on a sample of 150 MSB that provided information on the magnitude of outflows of money in HMRC’s recent research into Money Transfer Organization (MTO) activities, it is possible to derive an estimate of total outflows of remittances from MSBs outside the banking sector.
There are other factors that could explain the high figure. The data is based on the information which was provided by the trade and which was not subject to verification by HMRC officers. Also simple average figures have been used which can be skewed by a small number of exceptionally large figures. Another distorting factor is that the sample has a greater proportion of London businesses than the trader population as a whole. There could be double counting, especially given that smaller MSBs send money through larger MSBs.
Importantly, this figure relates to flows out of the UK to all countries, not just developing countries, so contrasting it with other figures is not comparing like with like. Although these factors are not likely to invalidate the information in the report as a whole, they do have to be taken into account when interpreting the data and may have resulted in a higher than expected figure for the sector as a whole.
This estimate is a greater figure than the total above. It is likely to include all cash transfers that MSBs undertake, not just migration remittance flows. For example, it could include charitable donations and business-to-business transactions (for those customers who do not send money directly via bank accounts). While MTOs may use banks to transmit the remittances they receive from customers, the estimate does not include money sent directly through the money transfer products offered by banks to their customers, and nor does it include flows through informal channels.
The market is consumer base sending money to EU and rest of the world, etc. and originating MSB clients which provide a diverse range of financial and non-financial business services in local, regional, and international markets. Financial activities include money exchange transactions and funds transfers. International MSBs connect the domestic financial system to the rest of the world. MSBs have traditionally been founded to correct a market failure – the lack of financial services for individuals of modest means or for small business owners.
HIRETT is located in London, UK. However, utilizing the latest technology and a network of correspondent financial institutions, the Company intends to service customers based mostly to EU and Rest of the world. The Company established online presence by Web based applications and Mobile Applications worldwide over the next 2 years of operation.
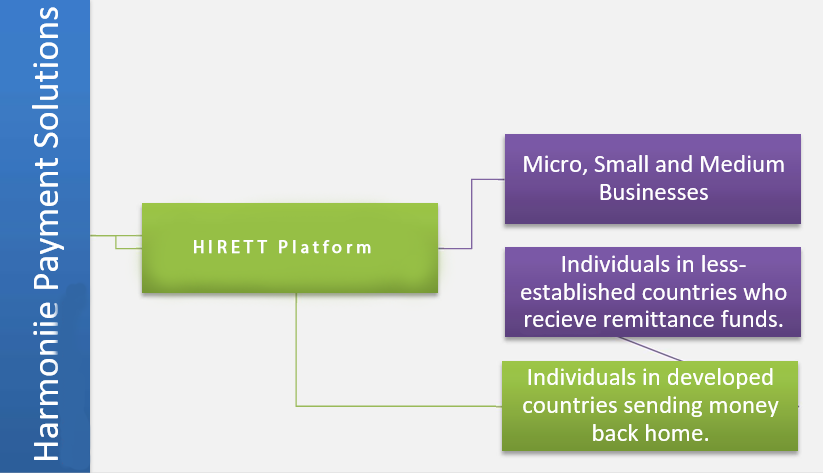
Key Target Markets
Through the Hirett and HIRETT platform, Hirett will service a large number of global clients as both a B2B and B2C service provider. The following visual will outline the key target markets for each of these platforms.
Customer Persona
With its expanded services, Hirett will seek to serve a market of high-risk businesses who have a driving need for a payment processing service. The following subsections will describe three fictional but ideal consumers who would benefit greatly from HIRETT’ new solutions.
2.4 Source of Capital
HIRETT was capitalized with funds from its Initial Investment, ongoing operational and venture capitalist.
3.0 Marketing Plan
This section provides the outline of the marketing plan of HIRETT for its E-money, Payment and money transfer services. It will increase its market share through targeted advertising to increase the number customers who are looking to save money on prices, reliance on services and high quality customer services.
3.1 Situation investigation
HIRETT is in money services business since its incorporation. And since its inception it builds a solid customer base through their high-quality customer relationship and innovative advertisement. The Company believes that the market demand for their services will be great and are convinced that a consistent marketing strategy is required for the company to expand its business in line with their strategic strategy. The company offers the money services and ticketing services in the UK. It will launch E-Money services and new payment services for its existing customer base.
3.1.1 Market Summary
The HIRETT provides variety of product regarding their market and target segments that they wish to provide serve.
3.1.1.1 Market Demographics
HIRETT possesses good information regarding their market and the target segments that they wish to serve. It will leverage this information to better understand who is served, their specific needs, and how the company can better serve them. The profile for HIRETT’s customer consists of the demographic, and behavior factors from male and female who will be over 20 and economically conscious of good deals.
3.1.1.2 Market Trends and Needs
The whole money services business industry has pressure being applied to them from different sides to achieve cost efficiencies and to decrease the cost of the various products/services and also to improve the customer services so that customer are getting right service from them. Over the last
4 years business have been faced a widespread consolidation to achieve costs efficiencies. HIRETT is able to coexist in this consolidation environment by achieving through their unique business model.
As a result of the recent economic recession, most companies are reluctant to offer lower fees and price. This has in turn resulted in increased need to meet customers demand. By identifying the gap in the market for provisions of such service, HIRETT is able to gain competitive edge over its rivals. The company offers its customers with a wide variety of attractive packages which are not only flexible but also tailored to customer’s needs.
3.1.1.3 Market Development
The industry is predicted to continue its greatest growth.
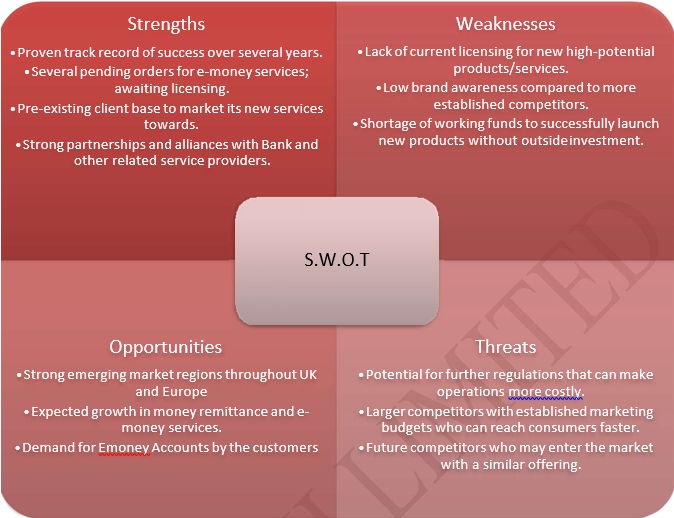
3.2 S.W.O.T Analysis
The following visual will display HIRETT t/a Hirett’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
3.3 Rivalry
The competition in the money services business is quiet intense due the large number of companies offering the services. This ranges from national chains Tide, Gocardless, Monzo, Metro, Barclays, Nat West & HSBC), building society, EU Banks operating in UK, Foreign Banks, internet based baking and retail banks and other private money services companies.
Competitive Analysis

| Description | Hirett Payment and it’s new platform, Hirett Payments, offers several payment services for businesses, and also offers low-fee money remittance for people who are sending funds back to their home countries. | WorldRemit is an online service that allows people to send money to friends and family living abroad. | Realex Payments is a European payment service provider and a division of Global Payments Inc.; one of Europe’s leading
providers of ecommerce payment solutions |
Azimo is an online international money transfer company that focuses on lower costs, and excellent exchange rates. | |||
| Year Established | 2015 | 2010 | 2000 | 2012 | |||
|
Services Provided |
Online Gateway, Account, Remittance | Payment E-Money Money | Remittance online transfer. | and money | Payment gateway, managed gateway solutions and online payment processing | Online money transfer, remittance, and currency exchange | |
| Number Employees | of | 0-10 employees | 201-500
employees |
51-200 employees | 51-200 employees | ||
| Annual Revenue | N/A | £41 million as of 2016 | Unavailable | Unavailable | |||
| Offering High-Risk
Businesses? |
to |
No |
N/A |
No |
N/A |
||
| Offers Remittance below SDG
target of 3%? |
Yes |
No |
N/A |
Yes |
|||
Competitive Advantage
With it’s new services, HIRETT will set itself apart competitors; becoming a maximum payment solution that targets both businesses and individuals. Specifically, with the launch of it’s new services, HIRETT will have the following advantages:
- Wider Potential for Business Clients: Unlike competitor companies, HIRETT offers high-risk E-Money Account. Other businesses have extremely high qualification requirements, and thus, their potential for expanded business is narrowed. HIRETT on the other hand, will approach a much wider market of both highly qualified and businesses.
- Remittance Fees Under SDG Target: Money that is remitted internationally is usually done so to aid in the poverty levels of less-developed countries. High fees from competitors (some as high as 10% of amount remitted) means that recipients receive less funds; even though every pound and pence may be needed. To encourage low fees, a Sustainable Development Goal of 3% per transaction has been set. Not only does Hirett Payments meet this fee goals, it exceeds it greatly by charging a fee equal to only 1% per transaction. Positioned as a lower-cost competitor, Hirett Payments will attract many more customers who require a low fee for their remittance transactions.
3.4 Marketing Approach
HIRETT should adopt the market penetration and product development strategy by capturing current market share from other financial institutions and independent money services companies that have been weakening from the economic crisis. In relation to the Porter Generic model, HIRETT should aim at using a broad based differentiation strategy to capture market share from ailing financial institutions. The marketing objectives of the company can be summarises as follows:
- To increase the current market share by 2-5%.
- Increase the effectiveness of the company by attracting new customer with eye-catching prices and
- Rebuilding customer self-confidence through
- Construction up corporate
- Appeal the new customer and also make the existing customer loyal to Company.
3.4.1 Mission
HIRETT’s mission is to be the UK’s best independent money services company by 2025 with the service and innovative products that fulfils customer requirements. We exist to attract and maintain customers. When we adhere to this maxim, everything else will fall into place. Our services will exceed the expectations of our customers.
3.4.2 Market Positioning & Target Marketing
The main target populations for HIRETT are the migration people within the United Kingdom. A time wait of half a year would be enough to test the effectiveness of the product as a method to obtain a higher market share for services. Demographic segmentation on the other hand should be focused on age and income. Special attention should be focused on young migration individuals starting their career in UK and high net worth customers.
Positioning is the act of designing the company’s offering and image to occupy a distinctive place in the minds of the target market. Data taken from SWOT and PESTEL analysis of HIRETT enables marketers to define the points-of-difference and points-of-parity associations. Points-of-difference are attributes or benefits consumers strongly associate with a brand, positively evaluate and believe they could not find to the same extent with a competitive brand.
3.4.3 Strategies
The single objective of The HIRETT is to establish as the best money services in UK. The marketing strategy will seek to first create customer awareness regarding the products/services offered, develop the customer base, and work toward building customer loyalty and referrals. It will use advertisements to communicate the message. Advertisements will be placed in different venues depending on the target segment that is trying to reach. To reach the walk-in customers, advertisements will be run in store and road.
3.4.4 Marketing Mix
There is a unique challenge to marketers for marketing of financial services because financial services are intangible, inseparable and cannot be inventoried. An expanded marketing mix is required to fully answer the differences between product marketing and marketing for financial services.
Product
The product is the heart of the firm’s marketing strategy. Poorly designed service/products that do not create value for customers will fail regardless of how well the other factors are executed. The goal of the product element is to create a service concept that would offer more value to a market segment than competitors.
The Company will offer products and services that will be responsive to its targeted market niche. Media advertisements will be limited and targeted to the MSB/EMI industry. Over the next three years of operation, the Company’s proposed products and services may include the following:
- Money Transfers Bank to Bank
- Money Transfers Bank to Cash Pickup
- SWIFT based transfers Bank to BANK
Single Features:
- No fees for the money exchange
- Lower fees for money transfer overseas except EU, Asian and African.
- High quality and reliable service
Price
The pricing component plays twin roles for HIRETT in the sense that it must be able to first attract customers to purchase the service and also generate revenue for HIRETT. There are five main factors that influence pricing decisions, namely, profit maximisation, market-share expansion, survival, social thoughts and personal purposes.
Pricing and Positioning
HIRETT t/a Hirett offers a wide range of services to help businesses and individuals solve their payment acceptance and receiving issues. The Company positions its self as a lower-cost provider for many of it’s services with pricing that is under the competitive rate, and also below the Sustainable Development Goal of 3% (for remittances). The following table will outline HIRETT’s pricing strategy with its current and soon-to-launch services:
| Service | Service Description | Service Fee |
| E-Money Accounts Services Transactions | Clients are charged a small percentage fee each time a payment is processed. | 1-1.5% of each transaction |
|
Payment Gateway |
One-time fee for access to HIRETT’s payment gateway which allows e-commerce businesses to easily collect payments online. | £150 |
| Fund (Remittance) | Clients are charged a small percentage fee each time a remittance transaction takes place. | 1.0% of transaction |
| Direct Debit -Payment Collecttion | Collecting of payments mandate on behalf of
customers |
£.10 to £3 per transactions |
Place
The place element involves delivering the product element to customers through appropriate methods and delivery channels. Failure to make a service product readily available to customers would guarantee its failure regardless of how good the service product is. The HIRETT will provide the service from its office which is in a convenient place so that customer can easily find them. And they also provide the service through the online transfer by the customer directly to the company’s account which will save the customer to travel the company to send money overseas.
Promotion
The promotion depends on effective communications to bring awareness in the market of the service products offered by HIRET. The three objectives of the promotion are to gain the attention of customers, convince customers to purchase the product and provide additional information. Advertising is mass, paid communication that is used to transmit information, develop attitudes and induce some form of response on the part of the audience. The choice of media that would be utilised includes newspapers, magazines, outdoor advertising and the internet. Other promotional materials include press releases, posters and brochures.
HIRET has developed a website for the purposes of providing information on the Company and its products and services. In order to better meet the needs of its customers, the Company intends to offer products and services by electronic means.
3.4.5 Marketing Exploration
MSB/EMIs have become integral parts of immigration communities. Hundreds of MSB/EMIs employing thousands of workers have had their business Bank accounts and access terminated by commercial Banks without cause. In recent years, MSB/EMIs have noticed that many of the services offered by banks could also be offered by other MSB/EMIs. Therefore, demand for the services provided by HIRET is growing.
HIRET will be specialized in providing financial services to MSB/EMIs and Consumers will use the following tools to analyze and to explore the market:
- Inquiries with probable customers
- Collect catalogues, price lists and advertising material of potential players
HIRET intends to acquire and retain MSB/EMI customers with low overall risk as determined by the Company utilizing the FILMS business risk rating system described below. For those customers who are not considered low risk, it will perform enhanced due diligence. It will not accept any high risk customers that are not in compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Since MSB/EMIs have increased AML risk due to the primary nature of their business, HIRET will work with all potential MSB/EMI customers to educate them towards reducing the overall risk in their business. As these processes are implemented and MSB/EMI customers improve the risk profile of their companies the impact on the Company’s AML risk profile would be expected to diminish.
Marketing and Promotional Techniques
To reach its demographic market most effectively, HIRET will implement several online marketing and promotional techniques. Specifically, the Company’s marketing strategy will include a high focus on:
- Content Marketing: HIRET will seek to become an authority leader in the business payment and global remittance sectors by positioning itself with quality informational content. The Company will follow a “Customer Research Journey” to identify the questions that potential consumers ask from the time that they are first introduced to a E-Money Accounts Services, e-money or remittance service, until the time that they begin considering becoming a user of the service. Once identified, the Company will create informational content to answer these questions. As users continue through HIRET’ content funnel, they will become more trusting of the brand and will begin to perceive the brand not just as another payment solutions site, but as a knowledgeable industry leader.
- Promotions & Media Outreach: The brand will further its authority positioning by taking advantage of several promotional and media opportunities. This will help build brand authority, expose the brand to new markets and align the brand with other known companies and media outlets. Early on, the Company will seek to get mentions and links through:
a. Online Roundups and Aggregators: Informational content will be submitted to relevant roundups and aggregators that attract readers of a similar demographic.
b.Podcast Opportunities: Representatives of the Company will seek guest podcast opportunities to broaden its reach and earn more links back to the HIRET and Hirett Payments websites.
c. Guest Blogging: Relevant but non-competitive blogs will be sought, where HIRET’ unique industry knowledge will be helpful to the blog’s readers. This strategy allows the Company to reach an already established base of readers, with the recommendation of the blog host; who already has creditability amongst the reader group.
d. Social Media; Related groups on sites like Facebook and LinkedIn will be identified, where HIRETT can publish and promote its content, engage with community members, and drive new users into it’s content and sales funnel. - Search Engine Optimization: Each page on the HIRETT and Hirett Payments platforms (including blog pages) will be optimized for best performance on search engines for related chosen keywords such as “Send money to (preferred country) ” and other valuable search terms. The Company will seek to build a high overall website relevancy by creating strong pages that position it as the most relevant online destination for all things related to e-money, E-Money Accounts Services services and money remittance.
- Paid Search Ads: A third-party specialist will be hired on a contract basis to implement and optimize a high-converting paid search ad campaign. The Company will focus on both major competitive keywords, as well as secondary and long-tail keywords that have less competition and a lower per-click bid.
- Growth Hacking: HIRETT will combine growth hacking methods to spur the growth and usage of it’s new services. Recipients of money remitted will be required to sign up for a new account, allowing the Company to further contact them with services through e-mail campaigns and promotions. Additionally, the Company will introduce a referral campaign for remittance senders that allows them to receive five no-fee transactions for each new user that they recommend; after that new user has transacted over £150. This promotion will incentivize users to introduce and recommend the platform to their peers and associates who have a similar need for money remittance services.
4.0 Products and Services-Additional
The Company offers selected products and services tailored to meet the needs of its target market.
HIRETT plans to engage in consumer transactions via its software, Mobile and web-based platform. The Company plans to institute controls that will monitor and restrict account activity to prevent errors or irregularities. These controls will ensure that the Company’s accounts and records are accurate and reliable, the transactions are properly authorized, and assets are adequately safeguarded.
Additional other products may be offered in concert with an ongoing evaluation of market opportunities, customer needs, development of appropriate policies and procedures, and the hiring of experienced staff. However, the Company will not deviate from the parameters of this Business Plan. The Company plans to utilize the existing relationship and industry contacts of senior management and the Board of Directors to target business development opportunities.
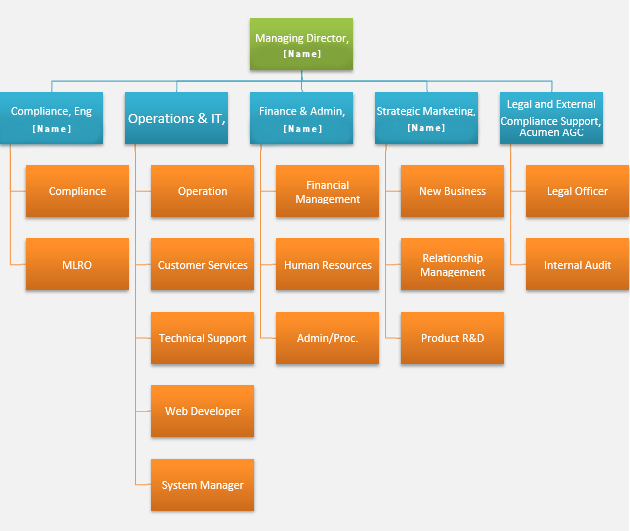
5.0 Organizational Structure
HIRETT governed by a Board of Directors that will include members with diverse backgrounds along with extensive administrative and operational experience in the EMI industry. The Company does not anticipate forming a parent holding company at this time. Also, the Company does not anticipate operating any subsidiaries at the present time.
Harmoniie will host a small but effective team; led and managed by it’s overseeing Director, [Name]. The Company’s organizational structure is presented in the hierarchy below.
6.0 Location and Office Structure
HIRETT is located at [Address].
7.0 Management Plan
7.1 Board of Directors
The Company has identified one individual to serve on its Board of Directors. Following is a list of proposed Board member and explanation of the responsibilities of the Company’s Board committee.
HIRETT LTD’s Board of Directors
[Name]
–Managing Director
[Name] is a successful businessman who is visionary and critical thinker. He has long standing experience in the business and by his dedication and noble guidance HIRETT became the successful venture. He is successful entrepreneur and passionate businessman who contribute in the community in greater extent.
The Board of Director plays a crucial role in providing strategic direction, supervision and support of Company management, and in attracting business for the Company through his personal and business relationships. As part of its responsibilities, the director will approve policies and procedures to meet all of the requirements of law and the demands of the Company’s Business Plan. The director will also retain a qualified external auditor and adopt strong internal control, compliance, audit procedures, and other risk management measures.
The Board committee structure will also serve to support the Company’s efforts to succeed in implementing and achieving its Business Plan.
Training and Knowledge:
Recently, he has taken Training from Acumen AGC and Acumen AGC on Anti-Money Laundering and Combat terrorist finance to gain necessary knowledge and fact about payments service business. In the training the following issues has been discussed:
- The identity and responsibilities of the Nominated Officer (or MLRO)
- The potential effect on the firm, its employees personally and its clients. / legal consequences.
- The risks of money laundering and terrorist financing that the business faces.
- The vulnerabilities of the business’s products and services/ Assessing the risk of money laundering in your business
- The policies and procedures that have been put in place to reduce and manage the risks.
- Customer due diligence measures, and, where relevant, procedures for monitoring Customers’ transactions.
- How to recognize potential suspicious activity.
- The procedures for making a report to the Nominated Officer.
- The circumstances when consent is to be sought and the procedure to follow.
- Reference to industry guidance Money Service Guidance and MLR- 9 and other sources of information, for example, NCA, Financial Action Task Force.
- Even he has read the following guidance to increase my knowledge and expertise to operate the business.
- E-Money Institution guidance –prepared by HMRC.
- PSRS-2017 the FCA Guidance, Applicable laws i.e MLR-2017 from section 5 to 21.
Experience:
Even he has relevant experience on the payment service business. As he has worked in HIRETT as MLRO and my main duties was below:
√ Supervising the compliance of the business.
For More: Please see the CV.
7.2 Management
The strength of an institution’s management and board is one of the most important indicators of any Company. The Company’s management team will consist of qualified individuals to serve as executive officers and directors.
Abdul Rauf Awan serves as Director of the Company. He has reasonable experience in the EMI industry and global financial markets. He also has a proven record of administrative oversight, strategic planning, business development, and servicing client/customer relationships. Since his appointment, he is the principal architect of HIRETT.
The key functions and responsibilities for the senior executive position are summarized below:
7.3 Manager
Roles:
- Oversee the day-to-day management of the Company and provide leadership to management.
- Report the operating performance, financial results, and strategy execution of the Company to the Managing Director.
- Ensure there are adequate operational planning and financial control systems in place.
- Provide executive management input and assistance with establishing Board agenda and administering Board committee responsibilities.
- Ensure compliance with all regulatory management requirements and corporate governance standards.
- Develop and direct financial plans to support the strategic business plan, growth and market opportunities, and business development.
- Establish and maintain cash management policies and procedures, and ensure cash resources are available for daily operations.
- Provide direction to the investment management function in terms of portfolio analysis, process design, and reporting and controlling.
- Evaluate, integrate, and manage the Company’s financial, administrative, information technology, investments, accounting, and planning functions.
- Responsible for the all of the reporting of the Company’s fiscal operating results, such as accounting, budgets, and regulatory reports.
- Advise senior management and the Board on fiscal control and profitability.
- Prepare, present, and interpret financial reports.
- Manage the financial accounting functions including, general accounting and financial reporting, internal controls and regulatory compliance, risk management, budgeting and forecasting, asset-liability management, and treasury and investment management.
- Direct financial accounting department activities, and provide leadership, training, and supervision within the department.
7.4 Compliance Officer and Advisor
[Name] is responsible to ensure that HIRETT is able to comply with the regulatory requirements. Acumen AGC provides the compliance support services for the HIRETT. It will
- Oversee the Company’s AML compliance program.
- Coordinate the Company’s day-to-day compliance.
- Ensure accurate and appropriate regulatory reports are filed.
- Develops and coordinates plans to implement laws and regulations.
- Maintain the compliance library, policy and produces manuals, and training schedule for all employees.
- Prepares periodic reports to management and the Board as required.
- Develop and implement a detailed customer identification program and know-your-customer program.
7.5 Operations and Administration
- Develop, implement, manage, and continually upgrade customer operations servicing function.
- Oversee the creation and development of management information system in support of money laundering control and its integration into the overall compliance plan.
- Review and recommend system modifications for business processing.
- Identify and manage conflicts of interest.
- Assume critical responsibility for research advice and clearance, regulatory training, registration of approved persons, and money laundering deterrence.
- Monitor account opening and transactional activity.
Staffing & Training
HIRETT will create a full-service team to manage the growth of its E-Money Accounts Services and remittance platforms. Currently, there are several employees already positioned within the Company, including:
– Managing Director (Salary = £30,000 per year): Oversees the Company’s entire operation and leads the progress of the brand.
– Business Development Director (Salary = £25,000 per year): Oversees marketing, sales, and implementation of the general brand director.
– Technical Support (Salary = £20,000): Provides support to both the Company and its clients when technical issues arise.
The Company will increase its staff by two members within the upcoming months to balance out the team and better tend to the business’ needs. These new employee positions will include:
– Customer Service Representative (Salary = £15,000): Responsible for addressing any customer issues and tending to any customer communications through e-mail or phone.
– Web Developer (Salary = £20,000): To support and maintain all current Hirett Payment software’s, and improve the software over time with new features, functions and
Hirett’s staffing plan is represented in the table below.
| Employee Position Yearly Salary Month/Year to be Hired | ||
| Managing Director | £30,000 | July 2019 |
| Business Development Director | £25,000 | July 2019 |
| Technical Support | £20,000 | July 2019 |
| Customer Service Representative | £15,000 | July 2019 |
| Web Developer | £20,000 | July 2019 |
Purchasing Procedures
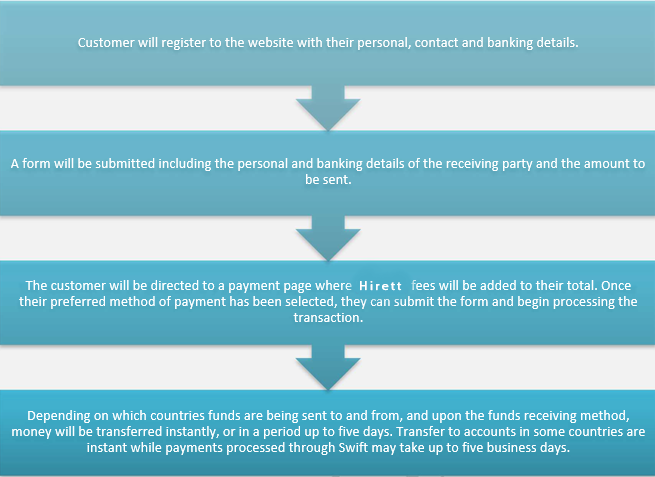
HIRETT LTD t/a Hirett seeks to make the process of E-Money Accounts Services approval as simple and quick as possible. To setup a HIRETT E-Money Accounts Services account, customers will follow the process below.

Hirett also makes it easy for customers who are seeking to send money through the Hirett Payments platform. The process for accomplishing a successful money remittance through Hirett Payments is as follows:
Customer Service
HIRETT t/a Hirett prides itself on the ability to exceed the expectations of its clients through both a high-quality offering, and a personalized and attentive customer service.
Customer service is managed by dedicated staff members who are trained to address any related situation. Hirett’ customer service department can be reached by telephone or e- mail. Support requests will be tended to immediately during normal business hours. By company standard, messages and e-mails received during non-business hours will be tended to within one business day.
Quality Control Measures
HIRETT t/a Hirett offers a highly-secure and reliable service to each of its clients and to its client’s consumers. To maintain a high-quality standard, the Company has implemented several measures into it’s system to monitor each transaction; analyze the associated risk; and automatically mitigate identified risks, when necessary. Furthermore, the Company’s software department will continuously test the software and make agile improvements to enhance the platform’s potential.
8.0 Records, Systems, and Controls
8.1 Accounting and Internal Control Systems
The Organizers of the Company have contracts with providers for data processing and item processing services to be utilized for serving customers, managing operations, and generating financial information. The selection was made by the Director, the physical security of the LAN and the controls used to ensure the security and confidentiality of customer and business information are regularly audited by information technology auditors who report their findings to the Audit Committee.
Accounting controls are established, documented and tested. The Company intends to engage A cumen AGC, or a similar firm, to perform regular internal audit procedures based upon a risk assessment. The company will issue written reports to the Audit Committee.
8.2 Internal Audit Function
The Company intends to contract with A cumen AGC, or a similar internal audit firm, to conduct the internal audit responsibilities. An internal audit plan will be prepared in conjunction with the hired firm, which will assign risk for each area/function of the Company, proposed testing procedures by area, timetable for completion of each respective area, and proposed implementing procedures for recommendations. The Company will conduct internal audit testing, by area, on a periodic basis to ensure all critical areas are covered on an annual basis. Internal audits will consist of procedures regarding accounting, internal control assessments, operational and regulatory issues. The internal audit and compliance will be checked and varied by the A cumen AGC. HIRETT chooses it because it has a wide experiences relating to compliance of money laundering and transferring and internal auditing, financial reporting and forecasting.
8.3 Compliance Management Program
The Company will develop a risk-based compliance program designed to ensure compliance with all Companying laws and regulations. The Company will utilize a third-party compliance firm to assist and complement the Compliance Officer. The Company has engaged A cumen AGC to assist in the development and ongoing revision of AML policies and procedures to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and best industry practice standards.
As discussed earlier, HIRETT will adopt a customer risk assessment protocol that follows a structure known as “FILMS” (comparable to the CAMELS program used for depository institutions):
- “F” represents the financial condition of the business; auditors review the balance sheet composition, profitability, capital level, and other elements in order to determine the business’s financial stability.
- “I” represents internal controls and auditing, an evaluation of the business’s internal policies and procedures.
- “L” represents legal and regulatory compliance, the critical issue of whether and how the business follows applicable laws, inclusive of AML.
- “M” represents the all-important management component, as auditors review the licensee’s ability to identify measure and monitor risk.
- “S” represents systems and technology, which is particularly important for money transmitters.
8.4 External Annual Audit
The Company will engage a well-known London-based accounting firm whenever the audit will be mandatory. The company is experienced in auditing financial services companies.
The Audit Committee will review the selection of the independent accounting firm with the Board on an annual basis. Services rendered by the independent accountants will include performance of the annual audit, preparation of income tax returns, and an annual review of operations and report to management.
8.5 Outsourced Functions
The Company will outsource its audit functions.
9.0 Financial Management Plan
9.1 Capital Goals and Objectives
HIRETT’s has capital of £360,000. The Company plans to comply with the regulatory requirements of the “well-capitalized” designation at all times.
HIRETT’s primary sources of capital originate from the initial stock offering, which it believes will support the Company through its next three years of operations without the need for additional capital. Alternatives for raising additional capital will be explored as the need arises. The Company would expect that a secondary stock offering would be the most logical avenue it would pursue to raise additional capital. The Company does not anticipate paying any dividends in the next three years of operation and will not pay any dividends until profitable.
9.2 Earnings Goals and Objectives
The Company expects to achieve positive earnings during its next quarter operation. The bulk of the Company’s revenue is projected to originate from Rebate, trading spreads and fees.
9.3 Capital Adequacy
The minimum target level of £360,000.00 in capital is more than adequate to support the level of staffing, the projected growth of the Company, the cost of technology, organizational expenses, and the limited structure of the Company. This finding is supported by the Company’s projections that are included as part of the Business Plan. The Company’s projections do not anticipate an additional need for external capital through the third year of operations. The Company does not plan any off-balance sheet activities that would affect its capital requirements.